Eventnet Support
VPN tunnel
What is VPN?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a technology that establishes a secure and encrypted connection over the internet. It protects your data, gives you more privacy and allows you to surf as if you were in a different location.
How a VPN works
Normally, when you use the internet, your data is transferred directly from your device to a website or service. However, this transmission can easily be intercepted or read, especially on public WiFi. A VPN ensures that your data is encrypted and transmitted through a secure "tunnel".
Clearly explained
Imagine the internet is like a road network where you drive from one website to another with your device. Without a VPN, you're driving on the open road and everyone can see your "license plate number" (IP address) and track where you're going.
With a VPN, you drive through a private tunnel underground. Nobody can see where you are going and your car number (IP address) is replaced by that of the VPN server. So you remain anonymous no matter where you go.
Technically, a VPN works by establishing an encrypted connection between your device and a VPN server. Your data is transmitted in a secure tunnel that protects it from unauthorized access. The VPN server then forwards your requests to the internet, replacing your real IP address with its own. This keeps your activities anonymous and your data secure, as it is only transmitted through this tunnel in encrypted form and cannot be viewed from outside.
Why do you need a VPN?
Vacation in another country
You are abroad and want to access your favorite series that is only available in your home country. With a VPN, you connect to a server in your home country and can watch the series as if you were at home, because the server retrieves the content for you on your behalf.
Safe surfing in the café
You're sitting in a café and using the free WiFi. Without a VPN, others on the same network might be able to spy on your data. With a VPN, you encrypt your connection and send it through a private tunnel - no one can read it.
Access to local devices
A VPN can be used not only for surfing, but also to set up a virtual private network. Imagine you're on a business trip and want to access a printer, camera or data storage device on your home network as if you were in the office. With a VPN, you can dial into your home network no matter where you are. It looks to your device as if you were actually in the office - you can use printers, folders or other devices as if you were in the same room.
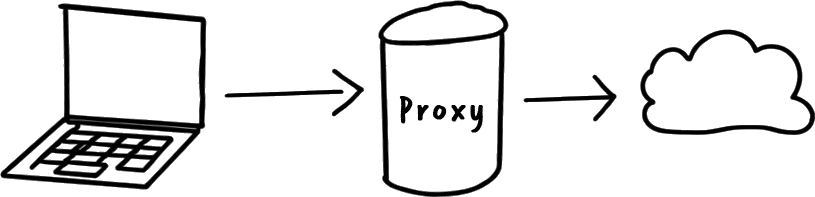
VPN vs. proxy server - What's the difference?
At first glance, a proxy server and a VPN appear to perform similar tasks, but technically there are crucial differences:
VPN
Encrypts your device's entire internet connection. This means that every application and service that uses the internet runs through the VPN tunnel. Whether you are using a web browser, a gaming app or a mail client - all data is encrypted.
proxy server
A proxy works at application level. This means that only the data that is sent via a specific application (such as your web browser) passes through the proxy. Proxy servers usually do not offer end-to-end encryption, which makes them less secure. They are often used to bypass geo-blocking or to browse the internet anonymously, but without the added protection of encryption that a VPN tunnel provides.
Conclusion
A VPN offers you a secure, encrypted connection over the Internet, protects your data from prying eyes and gives you more privacy. It differs from proxy servers in the more comprehensive encryption and security it provides for the entire internet connection. It also offers the ability to create a private virtual network to access local devices and networks from anywhere as if you were there.
If you value security and privacy or want to access local networks while on the move, a VPN is an extremely useful technology.